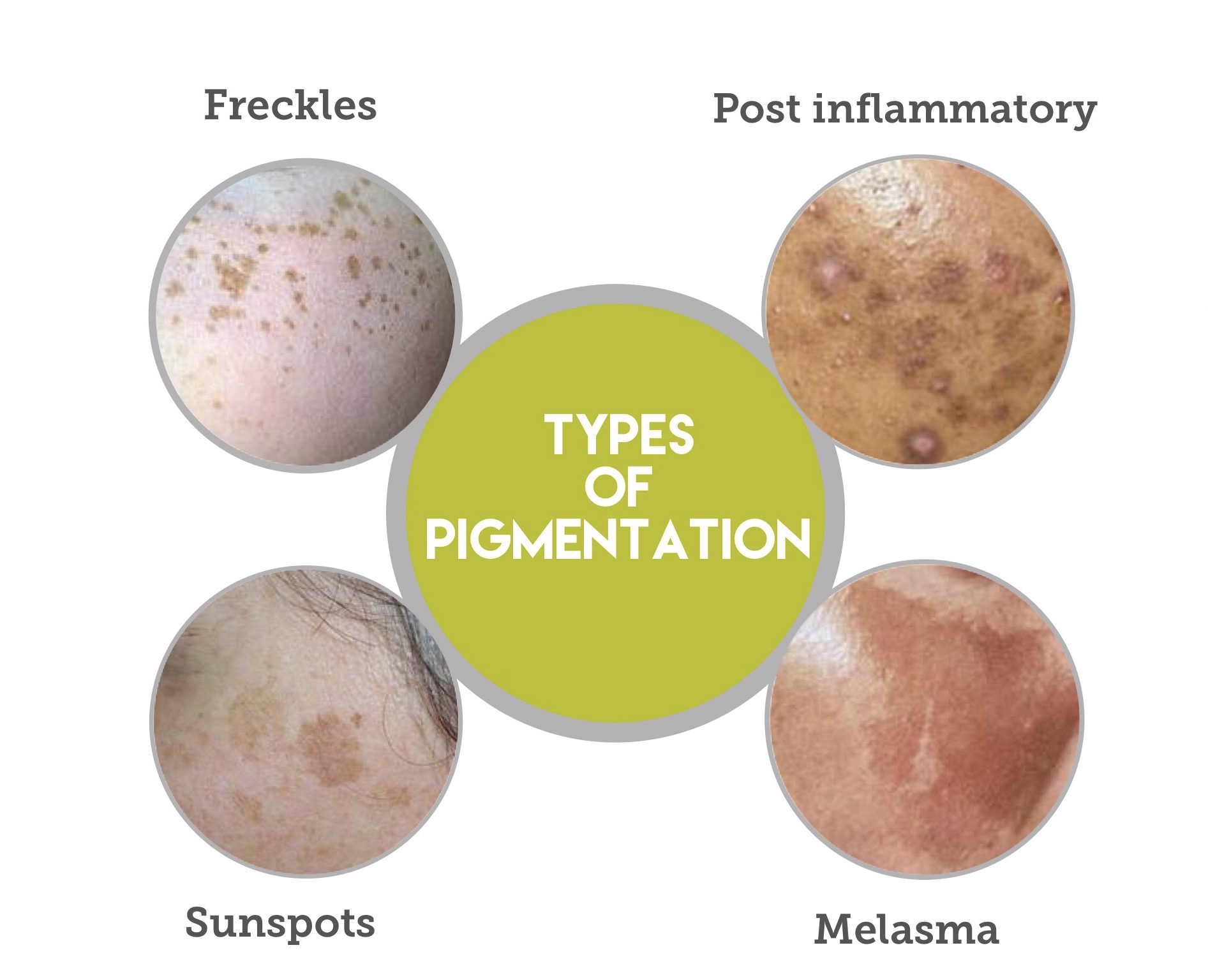
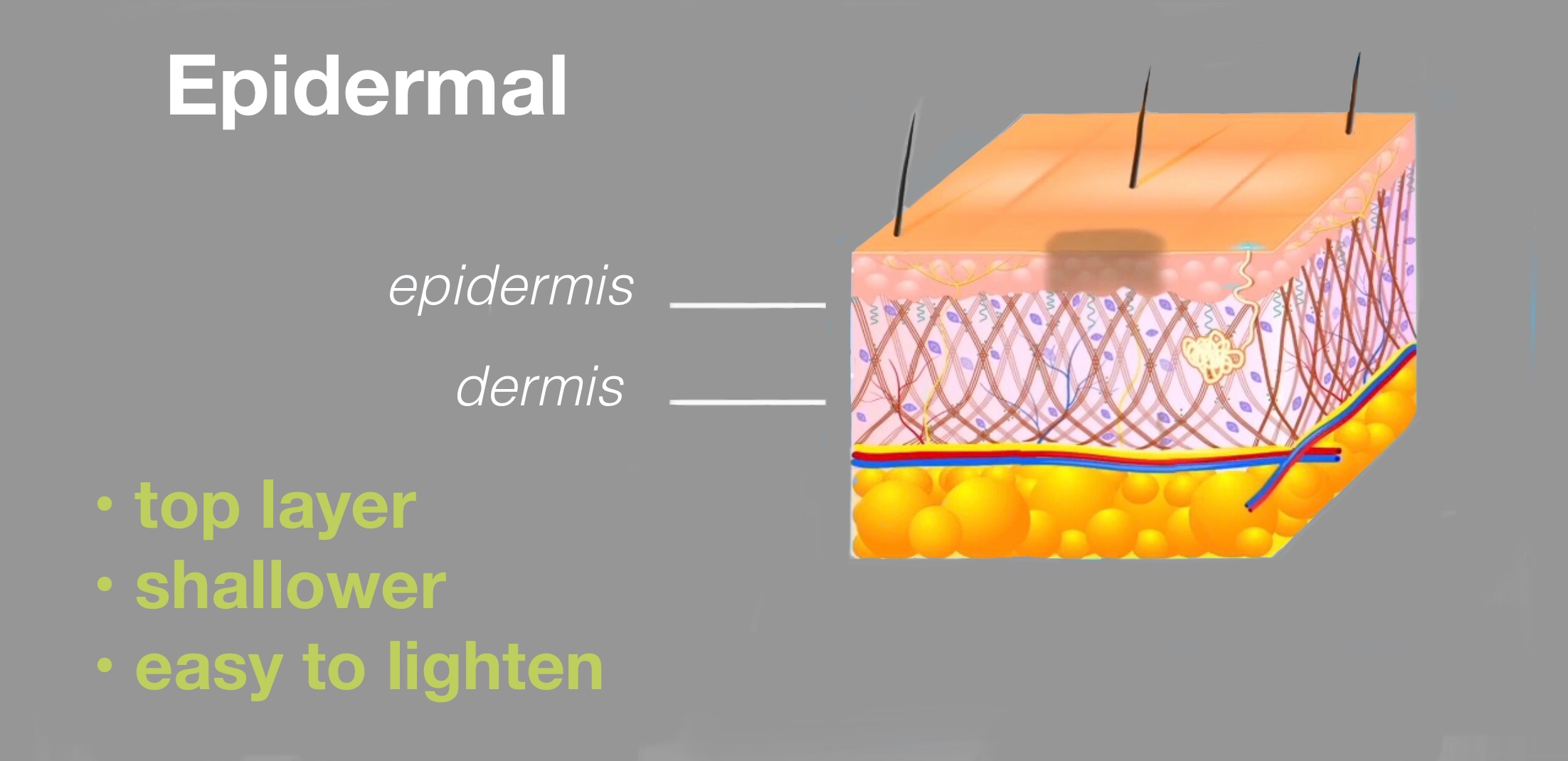
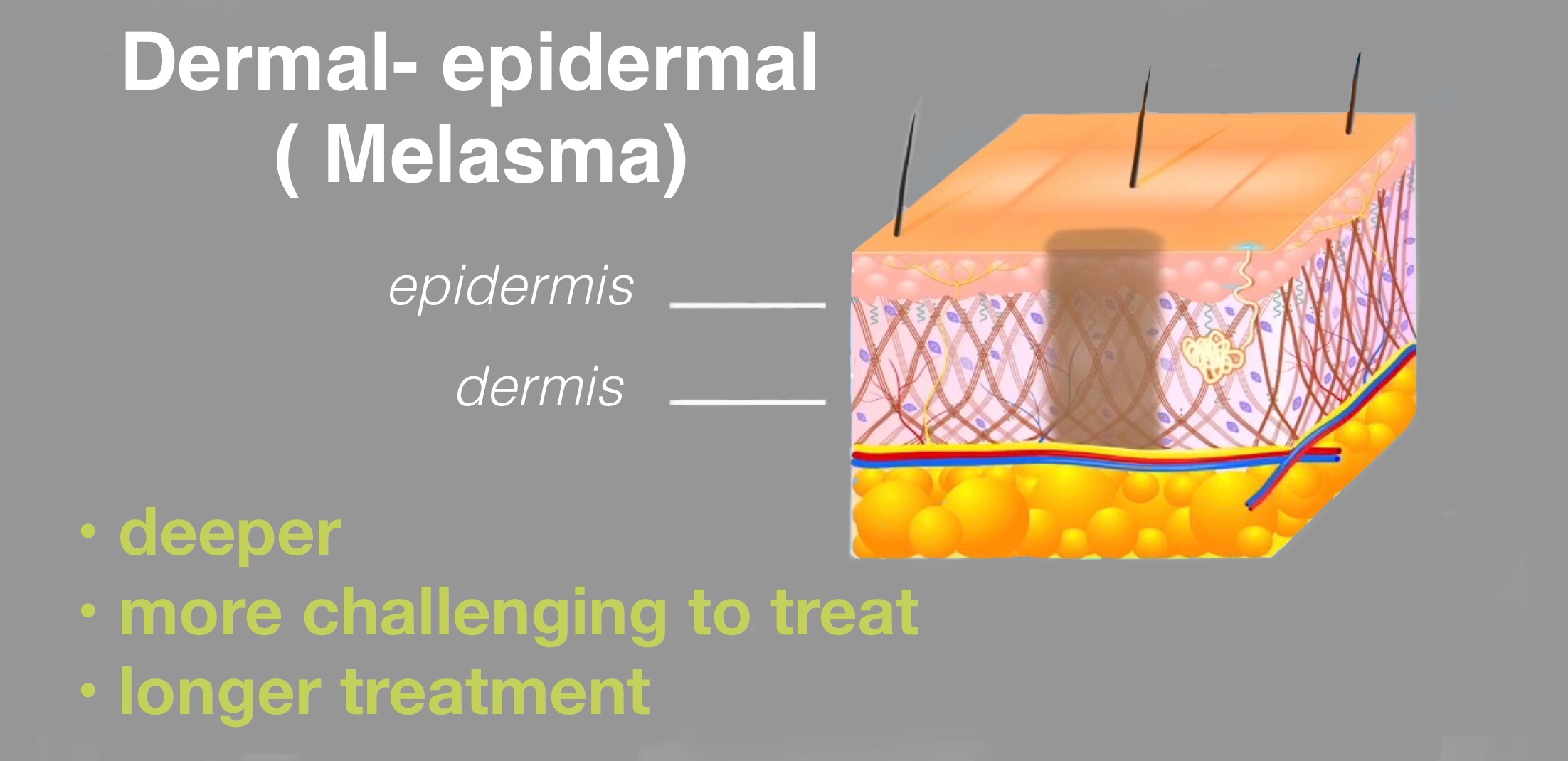
Pigmentation or hyper pigmentation is a term that is used to describe the appearance of dark spots, patches or even general darkening of the skin. The upper layers of the skin contains cells call melanocytes which produce pigment called melanin.
Human beings come in a spectacular spectrum of colours light, dark , freckled, auburn, blonde, brunette, grey or black hair. It’s amazing to think that this is due to a single type of pigment called melanin. The melanin is evenly distributed in our skin and gives us our skin colour .
Other than to colour the skin (plus hair and eyes), the role of melanin is to protect the skin – it absorbs UVB radiation from the sun. A sun tan (melonogenesis) is the result of higher melanin production, the body’s own defences against that damaging UVB.
Excessive skin pigmentation is a result of abnormal producti
on and deposition of melanin by the melanocytes. Production of melanin is dependent on UV or sun exposure, and is a natural protective mechanism of the skin.
Hyperpigmentation, areas that are darker than the rest of the skin, result from excess melanin production and deposition. This discussion will only encompass pigmentation that is in the skin, and will not involve discussion of raised pigmented lesions, moles, or skin cancers.
Hypopigmentation is the loss of skin pigmentation. This will not be discussed here.